What Is Cyber Warfare?
This can range from eradicating important computer programs, breaking into private files, or modifying the messages that are sent to individuals in order to change their opinions about something. What is cyber warfare, in its essence, if not these actions carried out on such a battlefield?
One should also mention that not all cyber operations can be considered as cyber warfare. Cyber warfare can be defined in the most specificity as the operations of at least two states or a large-scale organizational group with the primary purpose of infliction of significant harm with or without the intention of gaining something or achieving an objective.
This is dissimilar to cybercrime where the main intention is mostly to steal from the victim or cyber espionage which involves a breach of people or organization’s privacy in order to acquire information.
Importance of Cyber Warfare
Cyber warfare and ways of its prevention have become a critical question in the contemporary world of vast amounts of technologies. As brought by previous note, information literacy acknowledges that cyber-attacks are on the rise and even more complex as days go by. In addition, there are some analysts unequivocally sure that the future great powers’ war will start in cyberspace!
These attacks can be lethal and the ramifications are not seen in the abstract because they are known effects. Such a group can pose a threat to many countries’ national security, instill chaos in economic structures, and even kill citizens by targeting essential resources like electrical power stations or hospitals. Concepts like cyber warfare and the approaches to managing such kinds of threats are no longer amusements of the IT specialists, but things that we all have to be familiar with.
Do You Know?
Understanding Cyber Warfare
To understand the growth of cyber warfare and how the phenomenon should be prevented, it would only be relevant to establish how it originated and how it was developed.
Historical Context
Information warfare did not come to birth in one day. It exists as a result of computing history and has evolved with the world wide web. Here’s a quick timeline:
- 1960s-1970s: The history of computer hacking starts at this point and it is mostly for fun and to brag.
- 1980s: Cyber terrorism was for the first time launched through a state sponsored operation which targeted the Siberian pipeline.
- 1990s-2000s: Cyber threats are following the footsteps of the internet and unfortunately increasing with its progression. Governments have begun to pay attention, as many of these jobs are now being done and can be attributed to the public administration’s role in supporting modern civilized society.
- 2010s: The history of cyber warfare is officially admitted as an actuality. Such large-scale cases as Stuxnet, a computer worm that attacked the Iranian nuclear program, or Russia’s interference in extrarenal elections are massive.
- 2020s: Modern warfare would not be complete without the element of cyber warfare as this is again a common part of the strategies that most countries use in their defense.
2020-2024 Cyber Warfare Context
Analyzing the works of authors from 2020 to 2024, one can highlight the changes in the field of cyberspace warfare. The main factors affecting the confrontation are technology and geopolitics. Here’s a summary of the key developments during this period:
- 2020: COVID-19 Pandemic Impact: This forced change of working from home also experienced a 600% rise in cybercrimes due to the pandemic. The much ambiguity was seized by cyber criminals who subsequently attacked the weak systems and people.
- 2021: Ransomware Attacks Rise: Measurable attributes that become marked: There are more frequent attacks on high-profile targets; ransomware targets critical infrastructure. The increased frequency of attacks on infrastructures such as the Colonial Pipeline in May this year that affected fuel supplies in the United States, has brought focus on national security and distinct issues such as the need for cyberspace security.
- 2022: Increased State-sponsored Attacks: Other countries like Russia and China increased the level of their activity in the sphere of cyber operations. Preceding the commencement of the Russian-Ukrainian war in early 2022, the cyber attacks quickly escalated in the cyber sphere. The Ukrainians penetrated Russian governmental networks, while Russian hackers launched cyber attacks on Ukrainian ones.
- 2023: AI in Cyber Warfare: AI was first introduced to the framework of warfare related to cyberspace and it started to gain pace. AI tools were involved in proactive and tactical actions to increase the effectiveness of the state’s hackers and the penetration of protection systems.
2024
Major Cyber Incidents: Some noted cyber events were;
- Cyber Attacks on Governments: An attack was carried out by Chinese hackers in may 2024. In that attack, personal details of military personnel of the United Kingdom’s Ministry of defense were brought into the public domain. At the same time, Russian cyber spies are alleged to have struck Poland and Czech Republic; Malware assaulted Microsoft Outlook’s weak spots.
- Ukraine’s Cyber Offensive: Ukraine’s military intelligence hacked into Russian political organizations, presenting, thus the ongoing cyber war in the framework of continuing warfare tactics.
- Cybersecurity Developments: Germany said it will establish a specialized cyber military branch to deal with the growing cyber menace, especially from Russia. This step shows that cyber warfare is now seen as an important factor in the state’s security and defense policies
Trends and Observations
Global Cyber Arms Race: It is stated that approximately 46 countries are either developing or improving their capabilities of an offensive nature in the cyber domain, which highlights the new tactics and new areas of warfare with regard to the five domains of warfare.
Legal and Ethical Challenges: Some of these challenges touch on attribution in cyber attacks, whereby determining the parties involved becomes very complicated for international law and policy. Involvements of civilian targets with the military ones are murky and as a result, present continuously discussed topics in the international levels regarding the rules of engagement in cyberspace.
Economic Impact: Pertaining to cybercrime, it is expected to cost the global economy $10.5 trillion annually by 2025 Putting into consideration the magnitude of the losses, it is rather important to enhance cybersecurity globally, encompassing all domains of society. Learn more about the latest trends in data privacy.
In the strategy from 2020 up to 2024, cyber warfare is now embraced as a core component of the national security doctrines given the fact that states now appreciate the value of cybersecurity. Since technology is always changing cyber warfare techniques, plans, and tactics will also be changing thus the need for governments and private sectors to keep on being prepared and alert.
Why Cyber Warfare?
Why cyber warfare occurs needs to be known to reduce the chances of it happening. There are several main motivations:
- Political goals: Cyber threats as a nation might be used in the operation of altering electoral results, paralyzing governmental functions, or spying.
- Economic sabotage: The crises can be aimed at business or financial structures to inflict the adversaries’ economic damage.
- Ideological reasons: Other motives include advocating for change or achieving social upheavals since most groups with such motives attack bigger websites.
Types of Cyber Attacks
Based on the perspective of analyzing cyber warfare as a domain made up of its constituent elements, one can say yes to this statement since it can be used to describe virtually anything. Below are some of the well known types of attacks:
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks: These fill a system with traffic, and hence, make any operation in the system practically impossible.
- Malware and ransomware: A virus that can either compromise systems or freezes them before the user paid a certain sum of money.
- Phishing and social engineering: Strategies for apprehending a subject and getting him/her to give out information regarding a well-hidden fact.
- Data breaches: Mainly for spying, or to shame the organization, though this usually entails data stealing.
Learn more about the various cyber attacks.

- Lightning-fast speeds to browse without lag
- Servers in 105+ countries around the globe
- Military-grade security to stay safe online
- Try it risk-free with its money-back guarantee
- Native apps for all major devices
Pro Tip
The Landscape of Cyber Warfare Today
Understanding where things currently stand as we examine the new domain of cyber warfare and how it might effectively be defended is therefore imperative. Who are the key shareholders? Of what kind are those tools? And where is the major conflict taking place?
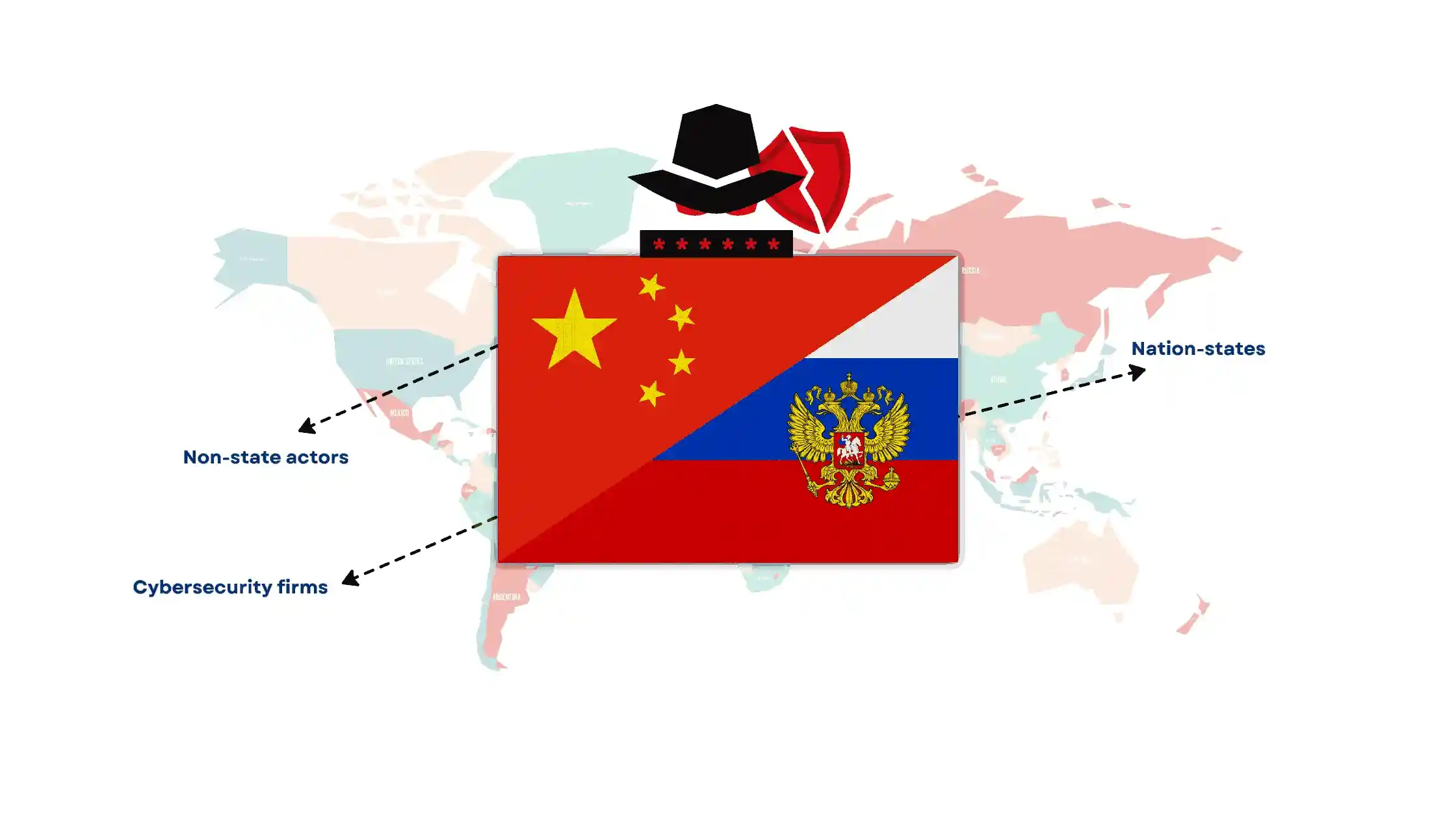
Actors Involved
The cyber space arguably encompasses the following characters of interest:
- Nation-states: The main actors of the cyber activities map include but not limited to; the United State of America, China, Russia and North Korea among others. A number of them have got distinct facilities at the military or intelligence level concerning cyber operations.
- Non-state actors: This concept of threat comprises terrorists, hacktivists which are activists who employ hacking to prosecute a cause; and organized crime groups. Again, they may not be as potent as nation-states but they are fully endowed to cause significant damage.
- Cybersecurity firms and researchers: These are the ‘‘good guys’’ involved in identifying, aversion, and containing cyber criminal activities. Another important use of teams is in countering cyber warfare, which is arguably a constant activity in the modern world.
Do You Know?
Tools and Techniques
The weapons that are being used in cyber warfare come in many different forms and the weapons themselves are not only vast but they are also evolving. Here are some of the key tools and techniques being used:
- Exploit kits: These are like toolkits for hackers which contain a set of strategies to exploit in the opportunities for making money for vulnerabilities of the computer systems.
- Botnets: A system of computers that are directly connected to the internet and infected so that the attacker can manage them.
- Zero-day vulnerabilities: These are the imperfections in the software which the maker of the software was not aware of and can, therefore, be exploited before the shortcomings are attended to.
- AI and machine learning: Both for the purpose of performing more complex and challenging cyberattacks as well as in the context of protecting from them. Learn more about the impact of AI on cybersecurity.
Recent Places of Information Warfare
Despite the fact that it is a global phenomenon, some regions are more engaged in cyber warfare:
- United States and China: These two superpowers are said to be spying on each other through the cyber arena and the victims could be from the government side to individual organizations.
- Russia: Being one of the advanced countries in cyber warfare Russia has reportedly meddled in elections of several countries through cyberspace.
- North Korea: North Korea is one of the least connected countries however over the time the isolated nation has built robust cyber warfare capability and frequently uses it for monetary benefits.
- Middle East: This region especially Iran has been on both ends of the stick as a victim and as an attacker.
It is a global problem to find the rise of cyber warfare and how to defend against it, yet these hotspots establish the character of these occurrences and advancements.
Impacts of Cyber Warfare
Information warfare is not limited to the Internet space as it has more serious offshoots for the countries that are involved. Let’s explore the wide-ranging impacts:
Economic Consequences
The financial toll of cyber warfare is staggering:
- Cost to businesses: Every year due to the cyber threats business organizations experience biggest losses in terms of money, time and their reputation.
- Impact on critical infrastructure: As has been seen from the recent past, a power grid, a transport system, or a financial system can be attacked leading to major economic problems. Learn more about safeguarding your enterprise against cyber threats.
Do You Know?
Societal Implications
These problems and others make cyber warfare raise legal and ethical questions. Sport plays a very significant role in people’s lives and it is currently being redefined. International law must accept the fact that many traditional concepts with regards to war laws are somewhat useless in today’s world of cyberspace.
- Erosion of Trust: Should such incidents continue, people may begin to contemplate on the security of Cyber systems. This could slow down advancement in technology.
- Psychological Effects: A lot of stress and anxiety is caused when hacking turns into a common affair and the details of people could be at the risk.
Legal and Ethical Issues
Cyber warfare raises complex legal and ethical questions:
- International law: It is important for one to know that most of the conventional legal dictee pertaining to warfare are hardly compatible with the cyber or cyberspace. For example, what is the meaning of the term ‘act of war’ with regard to cyberspace?
- Ethical dilemmas: Prospective actions move third to seventh accompanying the question whether nations should plan as well as acquire capabilities that are useful for attacking the adversaries’ computer systems or networks? Equality of rights is a highly protected right in every country, but how does this relate to protection of the nation?
Pro Tip
Protecting Against Cyber Warfare
Now that we have looked at an example of a new form of warfare – cyber warfare and its effects, it’s time to look at how one can prevent it.
The Role of Cybersecurity Measures
Cyber warfare cannot be won without prevention of cyber attacks. Here’s why:
- Proactive defense: Prevention is better than cure, it is always easier to avoid an cyber attack for privacy than to deal with a resultant aftermath.
- Deterrence: This is a major success because it is a lot easier to prevent the act than to react to it after it was executed by strong cybersecurity measures.
That is why it is said that in cyber warfare everybody is a candidate for being attacked. Everyone, including yourself, single persons, small businesses, major corporations, and organizations must protect themselves and ensure protection against cyber warfare.
Implementing Security Protocols
Here are some key strategies to protect against cyber warfare:
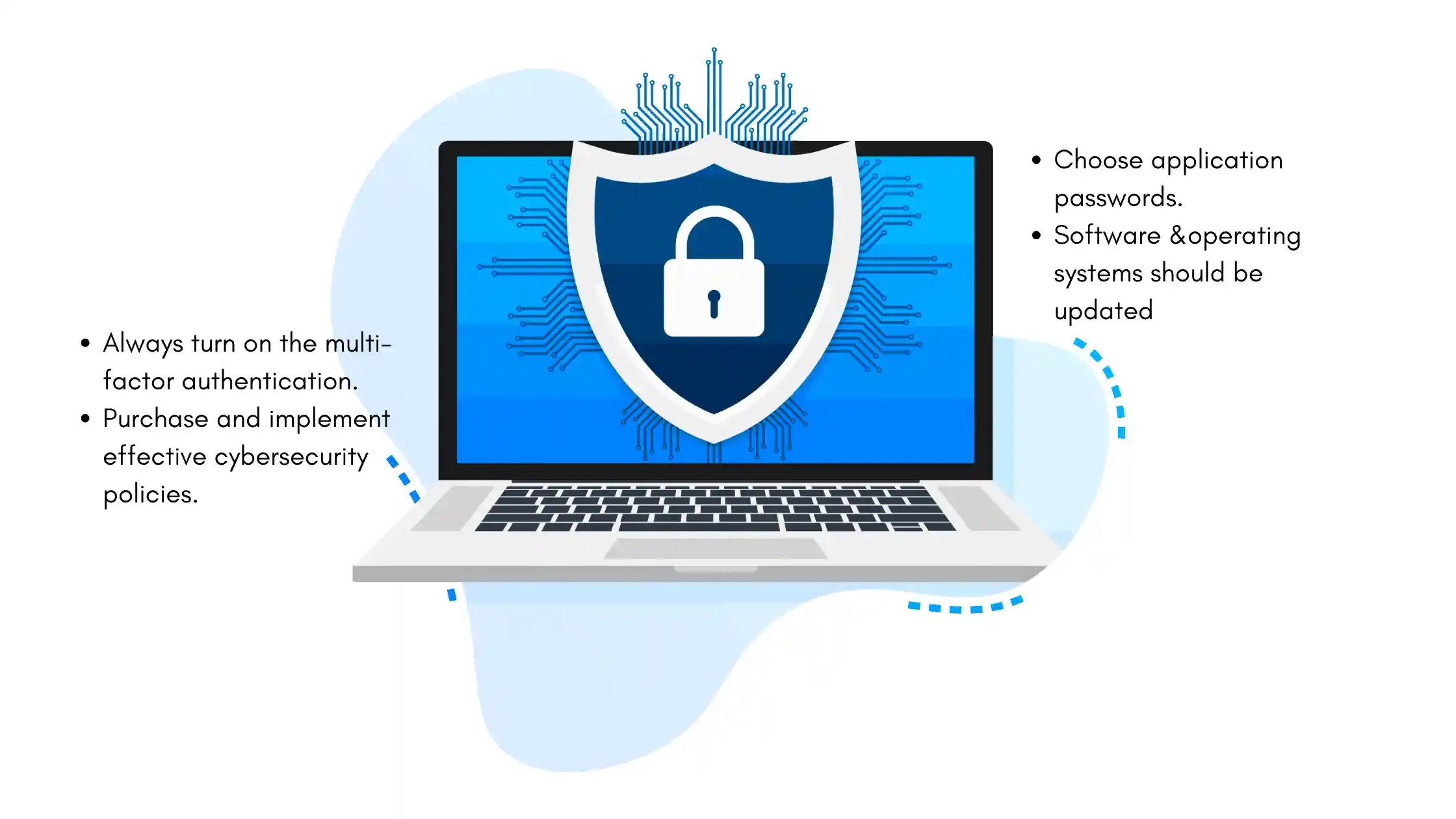
For individuals:
- Choose application passwords that are strong, and are not the same as passwords used with other accounts.
- Make sure that software and operating systems that are used are always updated.
- Avoid opening links or downloading any attachments from unknown persons or sending organizational sensitive information to unknown persons
- Always turn on the multi-factor authentication whenever it is offered.
For organizations:
- Purchase and implement effective cybersecurity policies
- Take security audit and penetration testing as a normal business practice.
- The fourth strategy entails training the employees on cyber security measures that are safe to use.
- There should always be an IRP ready in case an attack is launched.

Uninterrupted, high-speed browsing, zero logs so your online activity is always private.
Over 7000 people checked out NordVPN in the last month
Do You Know?
Government:
Governments play a crucial role in addressing the rise of cyber warfare and how to protect against it.
- Regulations: Currently, every government organization is implementing stronger measures in the protection of valuable commodities and data.
- Public-private partnerships: To fight against threats, governments are reaching an agreement with private sector corporations and organizations to collaborate in terms of threat intelligence more often.
- International cooperation: Governments and organizations are allying and trying to set the standards of conduct within cyberspace and to punish those that disrupt the peace.
Recent Update On Cyber Warfare
Chinese Cyber Threat: This was revealed by the officials in July 2024 that China based fully funded actors had taken part in cyber-attacks on Members of Parliament and the Electoral Commission. It has led to concerns about risks posed to British democracy and rousing to increase actions against such threats.
Cyber Command’s Stance: “We cannot afford to relax our guards because threats are on the rise for instance from countries such as China. This demonstrates an increase in the defensive approach in responding to the online attacks”.
Real Life Scenarios On Cyber Warfare, Including Recent Examples of Cyber Warfare:
Stuxnet (2010)
Stuxnet is considered to be the first cyber weapon that targeted physical destruction. It was focused on Iran’s nuclear programme and sought to destroy the machines, known as centrifuges, that are used to enrich uranium. The attack was said to have obliterated around a fifth of Iran’s centrifuges which sought to sanction how cyber warfare can successfully depose military objectives than resorted fighting in warfare.
The Russian Cyber Attacks on Ukraine: 2014-2016
In this period, Russia performed a sequence of cyber attacks upon Ukraine, and the most notable attack was the black-out of Ukraine’s power grid in December, 2015, in which more than 230000 people remained without electric power. These attacks were linked to other heists that were carried out during conflicts that have alerted the geopolitical position of Ukraine.
WannaCry Ransomware Attack (2017)
WannaCry is the worst ransomware attack in history which targeted about 200,000 computers in 150 countries by using a Windows vulnerability. It affected numerous industries and was catastrophic in areas such as healthcare by affecting the UK’s National Health Service (NHS). It also specifically brought out the flaws in the intellectual and technological security of vital organizations and the world web of cyber networks.
NotPetya Attack (2017)
At first, it affected Ukraine only, however, NotPetya became a global threat and losses equal up to $10 billion. It was intended to mimic ransomware, but the main goal was to cause damage – this weapon was most effective against Ukrainian and multi-branch organizations.
SolarWinds Hack (2020)
This was a complex and coordinated cyber spying operation through the manipulation of the SolarWinds Orion software where several entities within the U. S. government and other private entities were impacted. The attack is deemed to be launched by a Russian state-sponsored cybercrime and is ranked among the most severe cyber attack incidents in the recent past due to their impacts on the vulnerability of supply chain security.
Chinese Cyber Espionage
China has been accused of cyber spying and among the issues they have been involved in is hacking of the US office of personnel in 2015, where data of 21. 5 million personal records. Such attacks are typical to gather intelligence and stimulate interpersonal, group, and national competition among different countries.
The above mentioned scenarios illustrate the constant changes in cyber security strategies, in which state actors use technology as a weapon to achieve certain objectives, acts of sabotage, reconnaissance and information warfare. That is why these attacks’ consequences do not end with current harms, gaining traction in the sphere of national security and international relations. Find detailed information about privacy regulations on the internet.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What distinguishes cyber warfare from conventional warfare?
Who are the primary players involved in cyber warfare?
What can national managers do to protect against cyber warfare?
Can cyber warfare cause real time destruction to existent material objects?
How can cyber warfare affect firms and citizens?
What are some examples of cyber warfare in recent times?
Conclusion
This is a serious issue given the fact that cyber warfare is now a common phenomenon in our computerized enhanced society. They began with basic stunts on computers, but now they are affiliated with huge attacks on the countries. These can affect our money, our lives, and the way that nations come together.
Not cute at all, yet we can stand a chance and change this. Obviously, one has to know about cyber attacks, apply good safety tools, and everyone, from ordinary people to entire nations. This way the internet can be made safe for all users of the web and other computer facilities.
Being safe while using the internet is never set in stone because new threats are always created. This we will have to continue learning while being very cautious all the time. It is a requirement for all people no matter if they are computer literates or not.
In the same way, we need to apply the ideas of online safety as a routine shaped as locking the door at night. This includes refreshing some of our computer programs, finally agree to look at our privacy settings, and being cautious on what we have been doing on the internet. There’s nothing wrong with setting up combined and individual goals to achieve the desired safer online environment and experience for the present and the future generations.