Nevertheless, society today is more vulnerable than ever due to technological advancement hence the importance of good security measures.
Hackers are always inventing new ways of infiltrating organizations’ systems to access restricted information. That is why understanding what is a cybersecurity audit is one of the most significant factors that can make your organization’s protection reliable.

What Is Cybersecurity Auditing?
Cybersecurity auditing, often referred to as what is a cybersecurity audit, can be defined as a form of review of an organization’s information technology and systems, as well as its policies and procedures to establish gaps and risks, as well as conformity to industry guidelines.
It evaluates the efficiency of applying security controls and assists organizations in improving their protection against cyber incidents.
An audit can be internal, which implies it is done within an organization, or external, which means that it is done by an outsider, though an independent expert, to give recommendations on making a company’s security better in general, as well as to avoid the leakage of important information.
A. Purpose of Cybersecurity Auditing
The cybersecurity audit process is important in the following ways to any organization with the intention of safeguarding their information technology resources as well as conforming to legal requirements.
Identifying Vulnerabilities: Another purpose of the cybersecurity audit process is to identify vulnerabilities in the tested subject’s IT systems, the presence of which may indicate prospects for the success of an attack.
This results in proactive identification and therefore risks that are identified can be dealt with before they are exploited.
Ensuring Compliance: Cybersecurity audits involve checking whether or not the organization of interest complies with the laws and regulations in force, including the GDPR or the HIPAA.
The benefits of a cybersecurity audit include following legal requirements to avoid consequences and to keep the customers’ confidence.
Enhancing Security Posture: In addition to establishing a benchmark, audits reveal where improvements must be made since today’s threats are different from yesterday’s threats, and organizations need to respond to them adequately.
Improving Incident Response: The benefits of a cybersecurity audit also encompass assessing an organization’s incident response plan to determine that the organization has adequate procedures in place to limit risk exposure and assist with an aggressive return to normal operations.
Building Stakeholder Confidence: The proof of this could be in the form of audits done periodically; this shows commitment to the security of data, which in turn strengthens the bond of trust between the organization and its customers, partners, investors, and others.
Continuous Improvement: Security audits also entail continuous evaluation and enhancement of systems meaning organizations are always ready to meet new challenges that are ever present in a rapidly evolving cyberspace domain.
Thus, cybersecurity auditing plays a critical role in the detection of risks, adherence to the standards and frameworks, reinforcement of security.
And building the confidence of stakeholders about the company’s cybersecurity measures hence contributing to the improvement of the overall cybersecurity environment.
B. Benefits of Cybersecurity Auditing
Identifying Vulnerabilities: Security checks, specifically through cybersecurity audits, are important because they reveal the vulnerabilities of an organization’s systems, networks, and security measures so that those points that are vulnerable to cyber attacks can be dealt with.
Ensuring Compliance: Cybersecurity audits help organizations stay compliant with laws such as GDPR and HIPAA among others and avoid lawsuits and other penalties while building and maintaining a good relationship with customers and other stakeholders.
Enhancing Security Controls: Thus, cybersecurity audits make it possible to assess the current measures of security and compare them to the actual cyber threats, improving an organization’s protection and updating outdated measures.
Improving Incident Response: This form of risk management examines a company’s incident response plans for compliance and highlights the problem areas to help organizations be ready to deal with cyber threats and mitigate the consequences.
Building Stakeholder Confidence: Schedules audits are a shred of good evidence that an organization is concerned with cybersecurity; this in turn can enhance confidence among clients, partners, and investors because they know their identity and other sensitive information are safe with the organization.
Continuous Improvement: Cybersecurity audits make security consistently evaluated and modified, countering current threats and protecting organizations.
Optimizing Resource Allocation: Another benefit of cybersecurity audits is that they assist organizations in establishing the right priorities of security investments and ensure that the available resources are utilized appropriately depending on the security weaknesses and threats that are found.
These benefits underscore the importance of integrating the cybersecurity audit process into the security framework of an organization and confirm compliance with the current environment in this era of technology.
C. Steps in Conducting a Cybersecurity Audit
1. Plan and Define Scope
- Find out the objectives of the audit.
- Determine an exchange of the system, networks, and details of the processes that will be incorporated
- Identify the number of resources that will be utilized and the time duration for the audit.
2. Acquisition of Information and risk analysis
- Risk analyses should be conducted to see where possible threats and risks are in the organization.
- Employ tools such as the vulnerability scanner and Pen testing to identify the vulnerabilities that exist.
- Assess current levels of security control and cybersecurity compliance.
3. Review Security Policies and Procedures
- Evaluate the organization’s level of cybersecurity compliance with information security policies and measures.
- As a technical control, make sure that the right policies are developed, current, complete, and properly enforced.
- Assess physical control procedures, network security controls, application control procedures, as well as user control procedures.
4. Assess concludes outcomes and assess dangers
- Analyze the collected data to discover security threats and risks
- Raise potential threats’ probability and resulting consequences anticipation
- This means that risk should be ranked in an order of magnitude of the risk level possible or in other words the severity or frequency of occurrence of the risks.
5. Document Findings and Recommendations
- It is necessary to make a clear and concise audit report so that the findings should be easily identifiable
- These should also consist of suggestions on how the points mentioned can help to enhance the security situation.
- A plan on the manner in which the recommended changes are to be effected should also be given.
6. Follow-up and Monitor Progress
- Make sure that the organization has put in place the recommended improvement.
- Schedule an audit to determine the level of continuation toward cybersecurity compliance as well as the discovery of new risks.
By following these steps, one is in a position to carry out detailed cybersecurity audits and realize holes, risks, and possibilities for improvement for overall security.
Updating should be a regular process for effective defense against emergent cyber threats posing a threat to the firm. Audits are therefore very important.

- Lightning-fast speeds to browse without lag
- Servers in 105+ countries around the globe
- Military-grade security to stay safe online
- Try it risk-free with its money-back guarantee
- Native apps for all major devices
Best Practices For Cybersecurity Auditing
What is a cybersecurity audit? Cybersecurity auditing is a process where a cybersecurity auditor assesses an organization’s IT systems with the primary objective of determining areas that may require improvements in controls.
Possible risks that may occur, and the right approach that needs to be taken in handling the issues.
Establish Clear Objectives: This will require the setting of objectives of the what is a cybersecurity audit, such as if the audit will involve compliance, threats, or security control.
Engage Stakeholders: Talk to the organization’s IT directors, security officers or compliance officers so that all the stakeholders understand what is being audited.
Use a Risk-Based Approach: The organization should focus on those areas that are of paramount importance for the enterprise and which should be paid more attention and more resources.
Conduct Comprehensive Assessments: Identify all the forerunners of cybersecurity including policies, procedures, technologies, and physical security to examine the vulnerabilities in all the tiers of information technology systems.
Follow Established Frameworks: To plan the audit, it is better to adhere to the best practices given in professional cybersecurity frameworks and practices, such as ISO/IEC 27001, NIST CSF, or CISC controls not to miss any steps.
Perform Technical Assessments: Assessment and exploitation testing involving the assessment of risks in the IT systems and applications.
Document Findings and Recommendations: All the observations that have been made, all the potential and actual risks that were identified, all the key recommendations for improving the structure should come out clearly, and the language used to write them should be simple and understandable to the intended readership.
Implement Ongoing Monitoring: It is important to introduce a way to search for changes to the environment for threats and the corresponding vulnerabilities and to improve the effectiveness of the measures applied in the future.
Review Security Policies and Procedures: Banks that policies are current and applicable across the organization and this ensures that policies are up to date to change any should they be deemed irrelevant by the auditors.
Follow Up on Reactions: Depending on the findings of the developed audit, changes in the organization and implementation of the suggested changes.
In this way, it will enhance the results of the what is a cybersecurity audit, allow for the identification of the existing shortcomings, and thus, have a change tendency to enhance security.
Common Cybersecurity Audit Findings And Remediation

1. Weak Access Controls
- Lack of strong passwords: Enforce password standards that address issues like password length, their complexity, how often one must change them, and so on. Utilize the password managers in generating and storing complex and new passwords for every account created.
- Unrestricted access to sensitive systems: Organizational privileges should be accorded to the employees depending on their basic rights as employees. Also, conduct periodic access review processes and identify and eliminate excessive permissions. Make sure that logins to secure accounts are allowed to use more than one factor of identification.
2. Outdated Software and Applications
- Failure to update operating systems and applications: Perform periodic software scans to identify the applications that are installed in the computers. Establish patch management at the organization’s center and apply it in automation form wherever feasible. Prioritize patching critical vulnerabilities.
- Use of unsupported software: Create a strategy in migrating to newer versions or different software not supported by outdated software. Keep a list of the software along with their various versions and the corresponding end-user support life schedules.
3. Insufficient Network Security
- Misconfigured firewalls and network devices: Security policies and setup on the firewall should be checked from time to time as should the settings of the network devices used. One should apply the principle of network segmentation to restrict lateral movement. Enabling processing of logs and further monitoring for network devices.
- Lack of encryption for data in transit: Make sure that anything that is considered ‘sensitive’ is always protected with encryption if it will be passed through public networks. Take to the more secure standards such as Hibernate, SFTP, and VPNs.
4. Inadequate Employee Security Awareness
- Lack of security awareness training: Ensure that all employees have completed basic security awareness training where they need to learn about issues such as phishing, social engineering, weak passwords, etc. This should be accomplished through training sessions as well as practice in the form of simulated phishing.
- Failure to report security incidents: Implement unambiguous protocols of incident reporting and make sure that the employees comprehend these protocols about security threats.
5. Non-compliance with Regulations
- Lack of compliance with industry standards and regulations: It is important to periodically revisit basic and specific regulations and standards. The third sub-strategy under the second major strategy is to: General The power and authority of attorneys to practice before the Patent Office may only be exercised by attorneys in compliance with the provision of this order. Schedule compliance checks and assurance and get the employees acquainted with compliance with modern standards.
- Inadequate documentation of security controls: Secure proper documentation of the security controls, policies, and procedures that are being used. Documentation should not be hard to view for audits as well as compliance checks
These are the critical findings that organizations implement best practices by the cybersecurity teams to improve the posture and incident response in the case of a data breach and to meet regulatory controls and requirements.
Having an effective cybersecurity model in place for an organization is a critical aspect that needs to be prioritized especially for digital-based businesses. Here are the key steps involved in developing such a strategy:
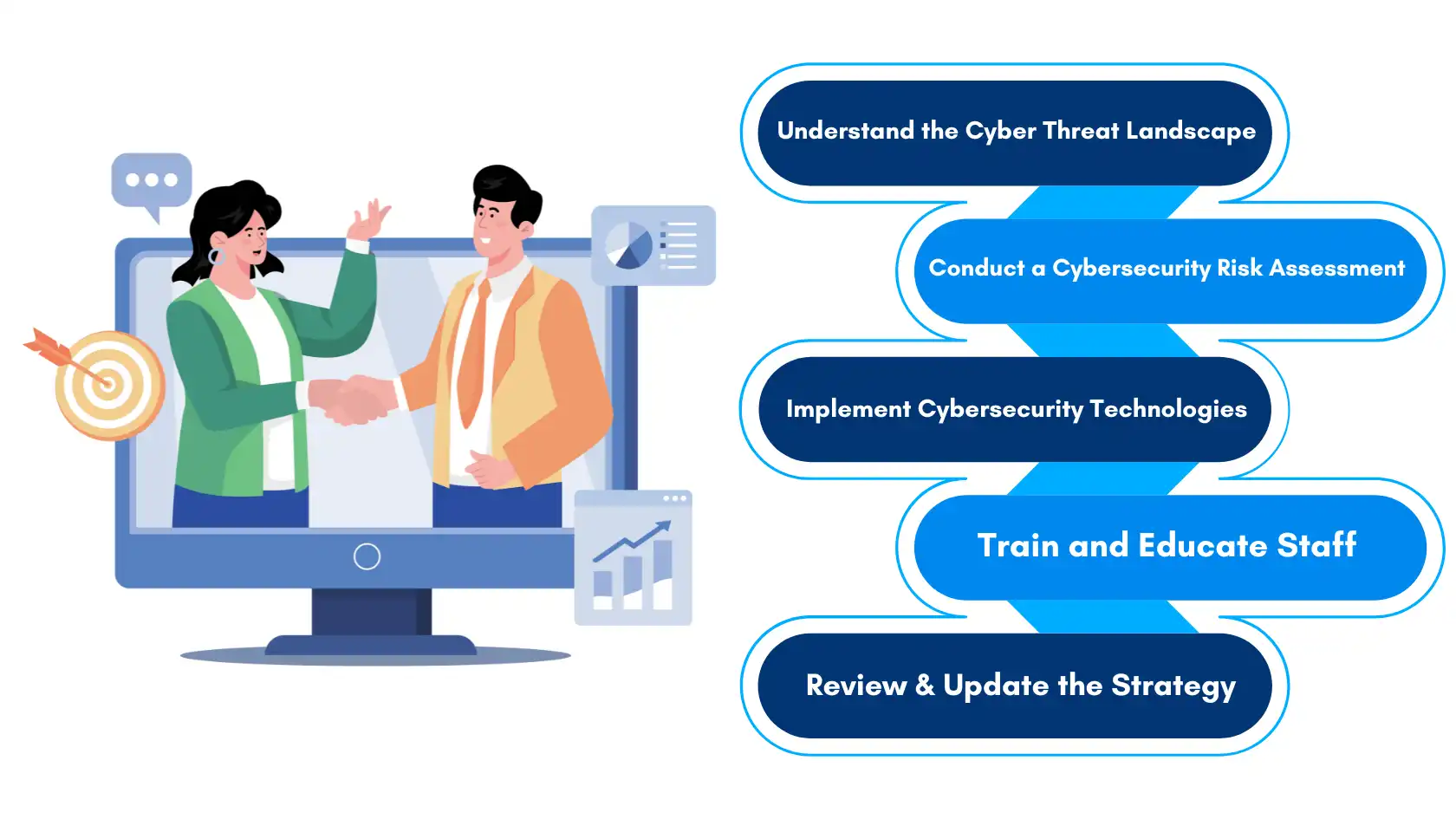
Steps To Implement A Comprehensive Cybersecurity Strategy

Uninterrupted, high-speed browsing, zero logs so your online activity is always private.
Over 7000 people checked out NordVPN in the last month
Understand the Cyber Threat Landscape:
- Identify the major threats posed by cyber disruptions, for instance, ransomware, phishing, and insider threats.
- Learn what new trends and risks exist affecting your security to avoid falling prey to any loophole.
Conduct a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment:
- Analyze and assess possible threats that can endanger your information systems and networks, as well as your information.
- Organizational risks should therefore be ranked concerning the level of risk they pose and their likelihood of occurrence.
Develop a Comprehensive Security Policy:
- Ensure you have a well-written security policy that gives guidelines, steps, and standards for security of the digital resources.
- It is crucial to guarantee the policy meets organizational requirements and is legal.
Implement Robust Cybersecurity Technologies:
- Use technologies that support enhanced security like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and encryption tools.
- It is suggested to switch to frameworks like Zero Trust Architecture or NIST Cybersecurity Framework to strengthen the security procedures.
Train and Educate Staff:
- Organize periodic awareness seminars or workshops to make the employees aware of the latest methodologies in cyber security as well as the possible risks involved.
- They should incorporate use of the simulations and awareness programs so that security becomes a more integral part of the company’s day-to-day.
Regularly Review and Update the Strategy:
- There is also the need to monitor how effective the cybersecurity strategy is, and if it needs some changes or improvements.
- It should also be remembered that it is imperative to conduct audits and tests periodically, including understanding what is a cybersecurity audit, to assess the gaps and risks that may have occurred or may be on the rise to determine whether the strategy will be relevant or not.
Establish Incident Response and Recovery Plans:
- Incident response management should also be properly defined to be able to minimize the consequences of possible security threats.
- Backup and recovery procedures should be implemented and these include regaining systems and information in the case of an attack.
Monitor and Improve Continuously:
- Make use of continuous monitoring techniques to be able to identify suspicious activities and possible threats at close range.
- Ensure that no company remains static but is often changing as new security threats and challenges are being developed.
Thus following these steps organizations can create a strong cybersecurity plan that will also take into consideration significantly developing new threats in the future.
Recent News Highlights The Importance Of Cybersecurity Audits:
Security Assessments Reveal Flaws in the System at Large-Scale Organizations
Marriott International: Another security breach that targeted the Marriott Company emerged recently when an audit exercise was conducted, and it was found that the company’s systems possessed gaps that any hacker could exploit to compromise them and steal personal information belonging to the clients.
This incident highlights the importance of understanding what is a cybersecurity audit to identify and address such vulnerabilities effectively. After the incident, the chain made changes to increase the security of personal information and also the frequency of security audits.
Capital One: In 2019, Capital One suffered a major data breach revealing details of more than 100 million customers due to which part of the blame was attributed to misconfigurations in the firm’s cloud-adopted environments. Such problems have been fixed in subsequent audits to address these risks
Recent Updates: Regulatory Agencies draws attention to Cybersecurity Audit.
NYDFS Cybersecurity Regulation: In particular, the New York Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) has recently enhanced its cybersecurity regulation: penetration testing has to be conducted at least once a year, while vulnerability assessments at least twice a year. The compliance of these conditions may lead to fines by the relevant authorities.
HIPAA Audits: This is especially true since the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has recently escalated its efforts in HIPAA compliance audits, meaning that healthcare companies must understand their security risks and properly apply safeguards to avoid compromising the privacy of patients’ information.
FAQs
What is a cybersecurity audit?
Why are cybersecurity audits important and necessary?
How frequently does a cybersecurity audit need to be done?
Who should perform cybersecurity audits?
Conclusion:
So speaking, understanding what is a cybersecurity audit is critical in helping organizations discover gaps, risks, and compliance issues to improve their security posture.
In this way, businesses can also make improvements regularly, prevent risks as much as possible, ensure that data is secure, and protect the consumer’s interest, which in turn would help strengthen organizations’ defense against this era of frequently changing cyber threats.