In today’s practically hyper-connected society where information is the primary fabric that ties it all together, ensuring the protection and safety of information has never been more paramount.
If you think about our lives as we speak, as we carry out transactions and as we produce and send documents, enshrouding all of these in a virtual veil of understanding that the next person can walk in and see is unimaginable. Ugh, it sort of gives one –shivers, doesn’t it?
In today’s practically hyper-connected society where information is the primary fabric that ties it all together, ensuring the protection and safety of information has never been more paramount.
If you think about our lives as we speak, as we carry out transactions, and as we produce and send documents, enshrouding all of these in a virtual veil of understanding that the next person can walk in and see is unimaginable. Ugh, it sort of gives one – shivers, doesn’t it?
But do not despair, my friends, for what is encryption? Encryption is the sword and shield of the digital world; it changes the fingerprint of our data into a fortress—a very complex one at that—and only the one who possesses the key can enter.
Encryption is the conversion of information into a set of symbols or codes that prevent easy understanding of the contents by any other person apart from the key holder.
Cryptography is the collective name given to various mathematical approaches useful in bringing about this transformation.
The actual data before the encryption is called ‘plaintext’ On the other hand the encrypted data is referred to as ‘ciphertext’.
Importance Of Data Encryption
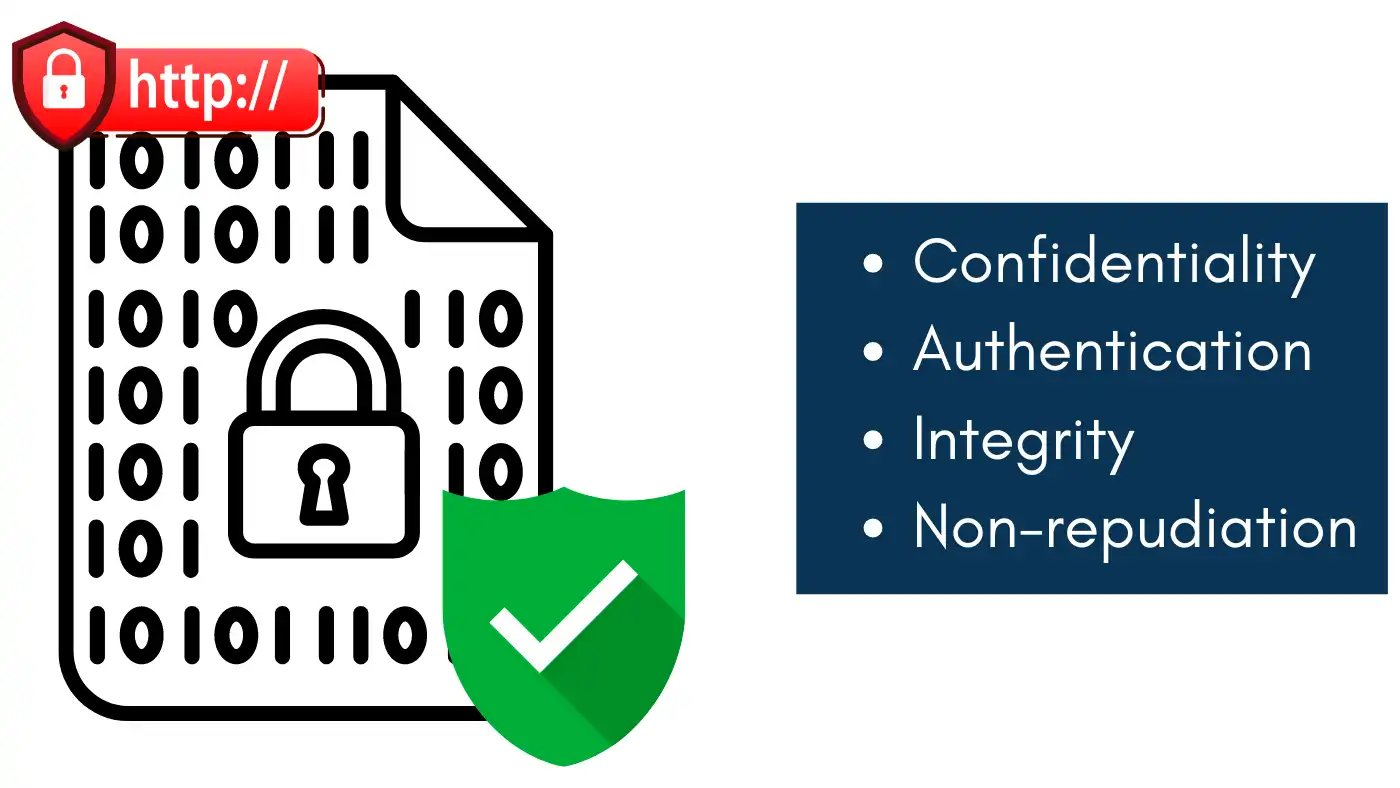
Security of information has become paramount in the current world where information technology is eminent; hence, the importance of understanding how does encryption work is very significant.
Its importance can be summarized in several key functions:
- Confidentiality: Encryption makes certain that data cannot be read by other individuals and or organizations if it is intercepted in the course of transmission.
- Authentication: It assists in authenticating the persons in the communication process; this assists in showing that the information comes from the correct source.
- Integrity: Encryption prevents tampering with transmitted data so certain that it is still of high quality. This is often done with the help of such other measures as message authentication codes (MACs).
- Non-repudiation: As the messages are encrypted, receivers cannot be accused of being involved in unwanted communication since messages are associated with senders.
As such, the importance of encryption is evident in various contexts, including securing electronic commerce transactions and safeguarding the transmission of sensitive data within corporations.
For example, in the process of buying something through the Internet, protocols of encryption prevent the ers from stealing the data of the credit card.
Hence, it is possible to conclude that encryption should be considered a significant factor in personal data protection and, in general, in the protection of data in a world where leakage or a various cyber threat is possible.

- Lightning-fast speeds to browse without lag
- Servers in 105+ countries around the globe
- Military-grade security to stay safe online
- Try it risk-free with its money-back guarantee
- Native apps for all major devices
How Encryption Works
A. Basic Concepts
-
Plaintext vs. Ciphertext
The Art of transformation of normal data or messages, which is in a normal form and easily understandable also called plaintext into an unfamiliar and confusing form called ciphertext is called encryption.
This transfer is done by using an encryption algorithm and a cryptologic key.
-
Role of Encryption Algorithms
Ciphers are complex mathematical equations that are used to transform the plaintext in a certain way to form the ciphertext.
These algorithms can be symmetric-key algorithms like Snowden which uses a single key or a pair of keys, one for the public domain and the other for the private domain.
-
Use of Cryptographic Keys
Keys are strings of characters that are used to decide on the sort of encryption that is to be used when encoding the data.
In symmetric encryption also known as private key encryption, the same key is used in the process of encryption and decryption of the plain text message.
Where one key is used for encryption the other is used for decryption, this is termed as asymmetric encryption.
B. Types of Encryption
-
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption, also called secret-key cryptography, is one of the types of encryption where the same key that is used for the encryption of data is also used for decryption.
The current conventional encryption algorithms used are AES and DES, which stand for Advanced Encryption Standard and Data Encryption Standard, respectively.
-
Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric encryption, also called public-key cryptography, uses a pair of keys: an exchange key that is used to encrypt messages in addition to the receiver’s key that is used to decrypt the messages.
Asymmetric refers to RSA and ECC, which are types of encryption, specifically Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC).
-
Hash Functions
Hash functions are one of the types of cryptographic algorithms that map the data of an arbitrary size into the data of a fixed size, which is called hash value or message digest.
While hash functions are employed to check the reversibility of data and integrity of records, and to identify any alteration in the records.
Thus, there is a reason to note that encryption’s main objective is to transform the plaintext into the ciphertext on the base of the encryption algorithm and the key.
In symmetric encryption, the participants use the same secret key for encryption and decryption of the message whereas, in asymmetric or public key encryption, the participants make use of one public key and one private key.
Hash functions play a key role as an intermediation layer in the sphere of data integrity since they compute hash values belonging to the data.
Applications Of Encryption
A. Data at Rest
Examples: Hard drives, databases
Encryption is utilized to safeguard information kept in numerous media types like hard disk drives, SSDs as well as databases.
This makes sure that there is no other means through which the data on a lost, stolen, or accessed by an illegitimate user device is readable without the inclusive decryption key.
Relevance to Information Security
The practice of encrypting data that is stored is very important owing to the increased risk that data face while at rest PII, financial data, and even intellectual property data are some of the data that need to be encrypted.
This assists organizations in getting around the legal requirements on data protection and reducing loss of data.
B. Data in Transit
Examples: Safe browsing: HTTPS, VPN, Secure Mail
Secure socket layering is critical for the protection of information that is transmitted over a network to prevent leakage of information. Common examples include:
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure): Applied when it is necessary to guarantee the traffic on websites while typing personal data, such as the login and the password, as well as to protect the payment data.
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): Provide encrypted links between the devices to enable users to access resources and securely communicate over plain and open networks.
- Secure Email: This respects the client’s right to privacy by allowing the encryption of emails and email attachments thus discouraging unauthorized access to the emails.
Role in Securing Communications over the Internet
It remains an intersectional constituent of holding the data confidential whereby information transmitted through the internet is encrypted to prevent it from being intercepted by other unauthorized parties.
It assists the clients to protect themselves from various cyber threats and risks that may include eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks as well as session hijacking.
Common Encryption Algorithms
The most common methods of symmetric encryption include:
Data Encryption Standard (DES): Data Encryption Standard (DES): It was developed in early 1970 and 1977 it became a recognized standard of the United States Government.
As for the DES key size, it was 56 bits only and in the current technological environment a minimum of 56 bits is not secure at all.
However, it was a great help in the formation of modern cryptography due to the efforts of the cryptographers to enhance the theory and build better schemes of encryption.
Triple DES (3DES): The next generation of DES worked on the cipher block of DES and used it three times in processing each data block that it encrypted then decrypted it back and then encrypted it again.
The method improved the size of the key and thus reduced the probability of deciphering the message through an attempt by guessing.
Despite this, 3DES is also widely considered a secure protocol and has been declared insecure by the US National Institute of Standards (NIST) for any software based from the year 2023 onwards.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): AES currently is one of the most preferred encryption algorithms that are in operation today; they were implemented by the US government in 2001.
This concept was developed with regards to a principle called substitution–permutation network. It is a block cipher of 128 bits, however, it is capable of supporting keys of 128, 192 ,or 256 bits.
Twofish: Twofish is widely used in both; hardware and software media; it is accepted as the quickest symmetric encryption technique.
Twofish is not patented but is not open source either, and it remains free for everyone to use.
However, it’s applicable in some of the generally used encryption programs such as PGP. It is possible key sizes may vary but can go up to 256 bits.

Uninterrupted, high-speed browsing, zero logs so your online activity is always private.
Over 7000 people checked out NordVPN in the last month
Pros And Cons Of Encryption

Pros
- Enhanced Security: Prevents all forms of digital violation from taking place as it safeguards and shields data.
- Confidentiality: Prevents other unauthorized people apart from the intended users from accessing data.
- Compliance: Fully compliant with legal data protection standards.
- Data Integrity: Checks data and makes sure that it has not been changed or tampered with.
- Remote Accessibility: Accessibility from different areas with high-security features enhances the safety of the users.
Cons
- Cost: May be rather costly when it comes to their application.
- Complexity: This cannot be handled by ordinary personnel but requires specialized personnel in IT.
- Key Management: Keys are used to open files and containers hence key loss leads to data loss.
- Performance Impact: These items might cause a slowing down of the overall performance of the computer.
- Compatibility Issues: That can disturb the present systems.
Case Studies
A. Recent Data Breaches
A breakdown of specific situations that could have been prevented or lessened in harm through encryption.
An example to consider is the Equifax breach of 2017 where the company suffered the compromising of personal details of more than 147 million consumers.
One of the main reasons behind this breach was the poor encryption of the information that is considered rather sensitive.
Hackers used a known vulnerability in Equifax’s website and stole in plain text consumers’ data, leading to cost the firm $700m and some of its reputation.
It is thus evident that, with the heightened sophistication of cyber criminals, it is imperative that strong encryption has to be put in place to safeguard any data and minimize harm that may be occasioned by malicious activity.
B. Real-Life Scenarios
While many people are aware of the potential for hackers to access messages in intermediary servers, few are informed about using encryption to implement that right in messaging apps.
Traditional media messengers such as Signal and WhatsApp have adopted end-to-end encryption that makes the message exchanged only readable by the sender and the intended recipient.
This encryption shields the users from interception and thus brings an aspect of security when people are being watched closely at a time when privacy is very much compromised.
Example of the Financial Institution Leveraging Encryption
An example where encryption was applied in a financial institution was through customer data protection; where account details and PINs are safeguarded in the course of transaction.
Through secure encryption measures, it was not only protecting the clients’ information but also meeting the legal standards – both elements built customers’ trust and minimized the chance of leakage.
From the above case studies, one can see that proper encryption of data can greatly minimize the consequences of a leakage of data, and contribute to the improvement of the protection of confidential messages.
Recent News And Developments
A. Developments in the sphere of encryption
Developments in Quantum Encryption
Quantum cryptography is gradually getting established as a revolutionary technique of data protection, especially in the face of emerging quantum computing threats.
It relies on the principles of quantum mechanics; one of the most comprehensive technologies that boast of security that cannot be penetrated.
The recent one is the quantum key distribution (QKD), as any attempt to intercept the key will noticeably distort the communication’s reliability.
New Encryption Standards and Protocols
To the existing threats from quantum computers, scientists are looking at post-quantum cryptography.
The goal of this field is to create encryption techniques that will be immune to attacks of classical and quantum types.
For the new algorithms, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is already employed in developing the specifications that would facilitate the adoption and implementation of these new algorithms into the current systems and protocols.
B. Legal and Ethical Considerations
Current and continuing discussions about encryption fallbacks for the police
People carrying out the discussion of black box encryption solutions are still a contentious issue.
Police and other law enforcement bodies claim that backdoors are required for both the protection of the country’s security and to be able to investigate crimes more effectively, on the other hand, civil liberties organizations say that they peril all users by making systems exploitable by any potential attacker.
More Current legislation that has an impact on encryption practices
Different countries are either planning or have passed laws that relate to encryption measures.
For instance, there are initiatives in some jurisdictions to legislate for the ability for law enforcement to have access to encrypted messages – though this has much debate about the invasion of privacy and data security.
These show the modern continuing growth and evolution of encryption technology as well as the perpetual accommodations between security law and ethics in the digital world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is encryption?
How does encryption work?
What are the common types of encryption?
- Symmetric encryption: Using the same key for encryption and decryption (e.g., AES).
- Asymmetric encryption: (e.g., RSA) – uses a public key for encrypting data and a private key – for deciphering it.
Why is encryption important?
Well, first of all, there is the data at rest and then there is the data in transit.
- Data at rest: Non-transitory tangible items (for example documents kept on a computer’s hard drive).
- Data in transit: Information transmitted over computer networks (for instance in the course of executing an online purchase).
Can encryption prevent a detrimental loss of data?
What are general encryption algorithms?
Conclusion:
Consequently, encryption can be described as one of the key means that ensures the safety of information in the sphere of digitalization.
With data converted into its unreadable format, encryption provides confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity for communication, data storage, and meeting regulatory requirements.
Looking at the future, as global technology improves, the utilization of encryption will turn out to be even more significant.