In today’s digital economy, the World Wide Web can be considered a crucial element in business and people’s lives. However, as much as there is reliance on these, dangers are there and the most prevalent one is the DDoS attack.
DDoS is short for Distributed Denial of Service attack. Specifically, it is a kind of cyber terrorism that generates abnormally large traffic to the targeted site or service.
In this article, the reader will learn what a DDoS attack is, how it functions, how to prevent DDoS attack, and perhaps more importantly, how one can guard against it.
DDoS Attack
A DDoS attack, short for Distributed Denial of Service attack, is a type of cyber terrorism where several computers flood a targeted site or service with abnormally large traffic, causing it to become congested and unavailable to legitimate users.
Suppose a number of persons have to come inside a small shop at one and the same time. I am personally advised the store bust-up and all persons get stranded outside.
Likewise, a site can be congested and halted whenever there are too many inquiries arriving at the same time. This illustrates how does a DDoS attack work.
How Does A DDoS Attack Work
Botnets: IDDoS attacks are typically executed using botnets, which are networks of compromised computers controlled by the attacker.
The botnets send a flood of traffic to the target, overwhelming its resources and making it unavailable to legitimate users.
These are general computers which contain viruses and malware that can be operated from outside the Computer’s own will. The attacker gives orders to the botnet controlling them to direct traffic to the given website.
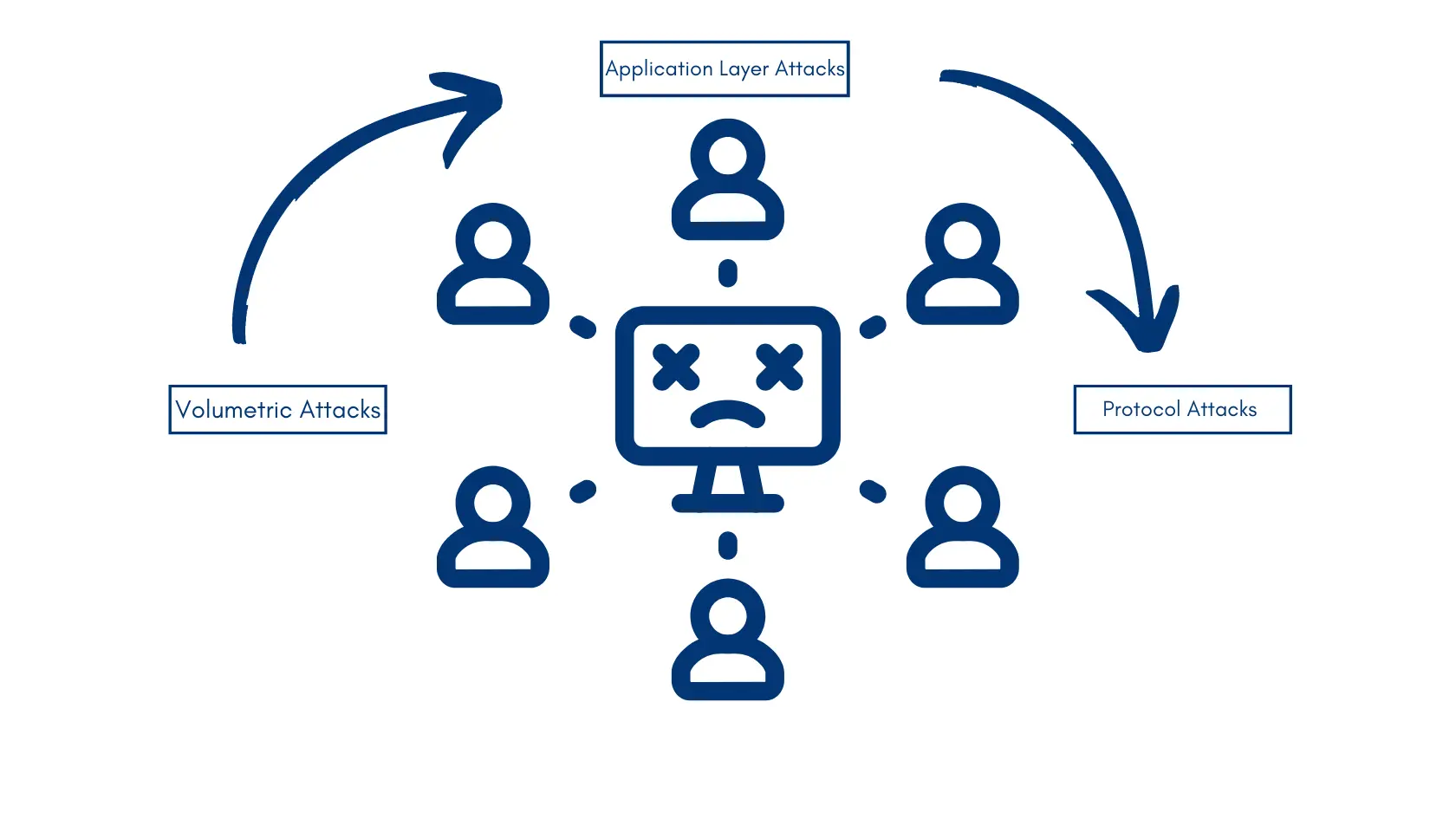
Many Faces of DDoS Attacks

- Lightning-fast speeds to browse without lag
- Servers in 105+ countries around the globe
- Military-grade security to stay safe online
- Try it risk-free with its money-back guarantee
- Native apps for all major devices
On the basis of approach, types of DDoS attacks are classified into different categories that differ in terms of methods and aims.
This information is important in the formulation of defense since there are different classifications on the subject.
Here’s a deeper look at the three main categories of DDoS attacks: The main types of DDoS attacks include volumetric attacks, protocol attacks, and application layer attacks.
Volumetric attacks flood the network with traffic, protocol attacks exploit vulnerabilities in network protocols, and application layer attacks target specific applications or services.
-
Volumetric Attacks
A volumetric attack is a type of DDoS attack that aims to overwhelm a target with massive amounts of traffic, making the network inaccessible to legitimate users.
Attackers often use traffic flooding and amplification techniques to increase the attack’s impact. Types of DDoS attacks include various methods that flood the target with excessive traffic.
How They Work:
- Traffic Flooding: In volumetric attacks, the attackers employ botnets, which are compromised computers, to send a flood of traffic to the target. This traffic can include ICMP pings or UDP packets for example Into small points or full points.
- Amplification Techniques: In most cases, the attackers employ amplification methods in order to enhance the impact of attacks. For example, they can initiate a small message to a third party server that will respond with a much larger message intended for the intended target. This method can greatly increase the number of visitants directed to the target.
Impact:
- Service Unavailability: The first objective of any method is to ensure that target’s services are inaccessible to users in the right society. When the values of these factors are greatly influenced by consumer reactions, this can result in large amounts of lost time and money for organizations.
- Increased Costs: Businesses can suffer other costs stemming from the allowed bandwidth utilization or negation of extra facilities to counter the attack.
-
Protocol Attacks
Protocol attacks exploit vulnerabilities in network protocols and aim to exhaust server resources rather than bandwidth.
Examples include SYN Flood and DNS amplification attacks, which cause the server to become overloaded and unable to respond to legitimate requests.
How They Work:
- Resource Exhaustion: The common protocol attacks are mainly made by sending requests that demand much computational time from the target server. For instance, the SYN Flood Attack relies on the TCP connection where the attacker floods the server with SYN connection requests but does not proceed to the connection completion stage leaving the server with half open connections.
- State-Exhaustion Attacks: These attacks can flood the server with traffic thus incapacitating it when it comes to state information. For example, a DNS (Domain Name System) amplification attack can use the DNS’s protocol, this causes the server to reply to a small request with a heavy amount of data and thus drain it.
Impact:
- Server Overload: Since protocol attacks focus on the server resources, It is easy for them to stutter or even stop which in turn hampers service delivery.
- Increased Latency: Regardless of the fact that the server may still function, the legitimate users will notice that the server has been highly utilized by the side of the attack.
-
Application Layer Attacks
Application layer attacks, also known as layer 7 attacks, target specific applications or services by exploiting weaknesses in a website’s applications.
These attacks often use legitimate-looking requests to bypass security measures and disrupt the targeted service.
How They Work:
- Legitimate-Looking Requests: It is an attempt made by the attackers to make the requests look as genuine as possible in order to have a sneak-creep through the application interface with the aim of allowing them to get through the cracks of the said interface.
For instance, a Denial of Service (DoS) attack may involve an attacker flooding a web server with a large number of HTTP requests to the extent that the server will be unable to respond to genuine users. Understanding how to prevent DDoS attack techniques is crucial for mitigating such threats.
- Slowloris Attacks: This technique entails initiating many to the target server and sending partial requests and keeping the connections open as long as possible. This occupies the server and can make a DoS (Denial of Service) attack in which the server can be unreachable for bona fide users.
Impact:
- Targeted Disruption: Application layer attacks are very damaging since they can affect isolated services like login pages or payment processing systems, they are direct consequences to users and companies.
- Difficult Detection: This makes it difficult to detect and prevent these attacks because they imitate normal traffic on the targeted network. Knowing how to prevent DDoS attack techniques is essential, as conventional security solutions may not be seen as threats to systems which enable them to operate without interference until they embark on a large-scale damaging spree.
Why DDoS Attacks Matter
DDoS attacks can lead to significant consequences such as loss of revenue, damage to reputation, and increased costs. They can make websites and services unavailable, causing substantial financial and operational impacts on businesses.
- Loss of Revenue: Sales originate from a website and therefore if a website is down, worries you cannot sell anything. Thus, for online businesses, even a couple of hours of the stop in performing their functions can lead to substantial losses.
- Damage to Reputation: Their expectations entail availability of websites. For instance, if a certain web site is repeatedly unavailable, then clients may lose confidence in the various products being provided by that company.
- Increased Costs: Some of the out-of-pocket costs could be of a recovery nature, for example, paying for specialists in the form of computer security personnel or new equipment.
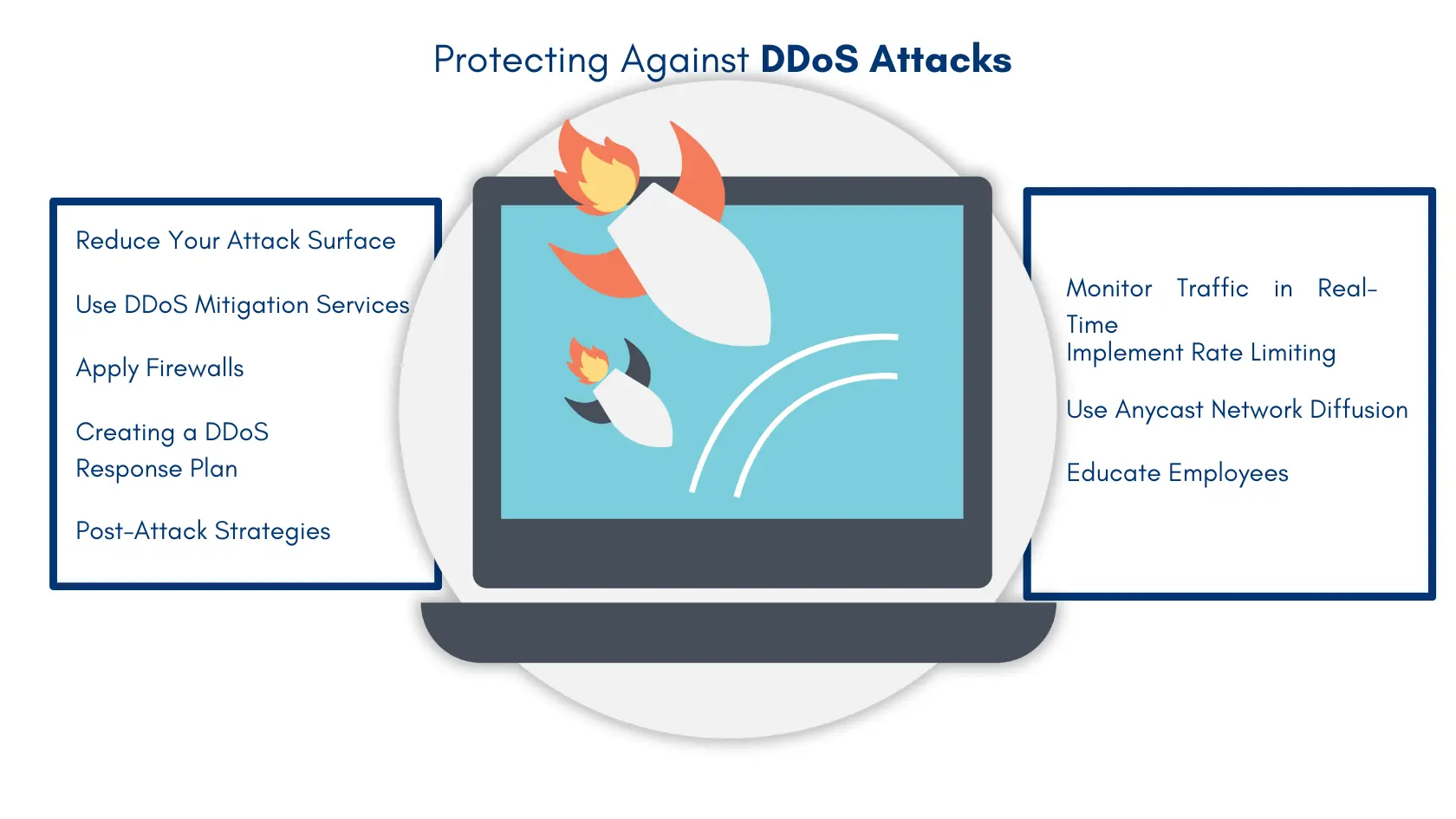
Protecting Against DDoS Attacks

Uninterrupted, high-speed browsing, zero logs so your online activity is always private.
Over 7000 people checked out NordVPN in the last month
Knowing what DDoS attacks are, as well as their importance, it is high time to discuss their prevention. Here are some effective strategies to prevent DDoS attack:
Reduce Your Attack Surface
The first line of defense is always to reduce the avenues through which an attacker can launch an attack. Here are some ways to do this:
- Limit Open Ports: Minimally, open only ports that are important to the running of the website or application in question. Every open port is a vulnerability that an attacker could and would try to exploit to prevent DDoS attack.
- Use Strong Passwords: Make sure all the accounts that you are using, especially those with privileged access, are protected by the strong and distinct passwords.
- Keep Software Updated: Change all the software- OS and Apps- as often as possible to cover up for all the open flaws.
Monitor Traffic in Real-Time
Monitoring the traffic of your network can also enable you to recognize changes in the normal pattern quickly. Here’s how:
- Use Monitoring Tools: Alas, it is not very difficult to find a tool that will help to monitor website traffic. Some of these tools can be used to notify you of traffic congestion which may be as a result of a DDoS attack. To prevent DDoS attacks, these tools are essential.
- Analyze Traffic Patterns: UTM can be useful for studying normal traffic flows; thus, recognizing an abnormal situation at the first sight.
Use DDoS Mitigation Services
There are many organizations that deal with fortification against DDoS attacks. Here’s what you need to know:
- Managed DDoS Protection: These services can assist in blocking out bad traffic before getting to your server. They employ sophisticated methods that would give a differentiation of good and malicious traffic.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: A vast majority of the DDoS protection services are run through the cloud. This means they are capable of handling a large number of hits and ensure your website is operational even during an attack.
Implement Rate Limiting
Rate limiting is the method used to limit the number of requests a user makes to a certain server at a certain time. Here’s how it works:
- Set Limits: It is possible to put the capping of the amount of the requests from a specific IP address in a span of a few minutes. This is because it helps restrict some users from thrashing your server.
- Use CAPTCHA: Specifically, CAPTCHA is used to protect from attacks where the attacker sends a massive amount of requests to your website.
Apply Firewalls and Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
In fact, firewalls are crucial network security accessories that you should incorporate in your network security system. Here’s how they work:
- Network Firewalls: These work as a shield between the internal network and the outside world, the World Wide Web in this case. They control the flow of traffic entering and leaving the network and reject anything that is in any way suspicious.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAF): WAF have specifically evolved for web applications. HTTP traffic can be filtered and monitored in and out of a web application; in this way, they can block unwanted requests.
Use Anycast Network Diffusion
Anycast can be used to possibly distribute traffic across multiple servers, although I am not fully certain of how it works. Here’s how it works:
- Traffic Distribution: Anycast on the other hand means that many servers will be having the same IP address. Requests made by a user are directed to the nearest server through the network. This is useful for sharing the load and can handle DDoS far better than if all of it was directed toward a single site.
- Improved Resilience: In case of overload one server will be able to redistribute load to another server while maintaining your service up and running.
Creating a DDoS Response Plan
A DDoS response plan should include identifying key personnel responsible for managing the attack, creating communication protocols for internal and external communication, and regularly testing the plan to ensure quick and effective responses.
- Identify Key Personnel: Entity: establish the team that will evaluate and respond to DoS attacks. It is vital that everybody is clearly aware of their responsibilities.
- Create Communication Protocols: Define channels of internal communication and communication with third parties in the course of an attack.
- Test Your Plan: Also, it can be necessary to practice to make it evident to your team that they have to act very fast.
Educate Employees
Educating employees on cybersecurity and how to identify potential DDoS attacks can help in early detection and prevention.
Regular training sessions and promoting a security culture can reduce vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security posture of the organization.
- Training Sessions: Ensure that there are periodic employee training and periodic workshops in order to refresh the personnel on issues to do with cybersecurity, specifically on how to identify and prevent DDoS attacks.
- Promote a Security Culture: Promote responsibility on the part of the employees for the security of the business. It can assist in avoiding mistakes that can create openings and this will enhance successful growth and help to prevent DDoS attacks.
Post-Attack Strategies
Post-attack strategies are critical actions and measures taken after a cybersecurity attack to mitigate damage, recover systems, and prevent future incidents. Here’s what to do:
- Analyze the Attack: In wound care post attack, recount the events that took place. The next step is aimed at determining the specific details of the attack and the specific weaknesses the culprits took advantage of.
- Update Your Defense: From this attack, lost feelings of invincibility and understand the need for much stronger protection. This may mean new releases of software, modifications to systems or acquisition of new tools for the security team.
Conclusion
Cyber criminals use malicious tactics, of which DDoS attacks are commonplace in today’s technologically advanced world.
However, you should understand how they work and, therefore, apply the right protection measures to prevent effects on your websites and services.
Again, the focus should be on protection from the onset, encased by defense in layers. You should update your defenses, track your traffic, and train your employees to prevent DDoS attacks.
Thus, it is possible to prevent oneself from becoming a target of a DDoS attack and protect personal data from being leaked.