What does HIPAA protect?” This is a question that we have been hearing for some time, and it well deserves to be answered.
We know that HIPAA is your personal health information superhero. Well, what exactly do they even do?
Basically, the HIPAA Privacy Rule is a shield that protects our sensitive health data from prying eyes.
The coolest part is to think of HIPAA as kind of a regulatory “good-news-bad-news”.
HIPAA not only secures your information but it also establishes you having a design over how that particular personal data can be used without violating any guidelines.
Ready to make a medical record request? HIPAA’s got your back. Must fix an error in your medical history? HIPAA’s on it.
At this point, you may ask yourself how HIPAA manages to do all of that. Well hang on because we are about to expose you, get backstage and show all the HIPAA privacy rule.
Historical Background And Evolution of HIPAA

Congress enacted the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act on August 21, 1996, to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the U.S. healthcare system.
The History, Background, and Evolution reflect its response to the growing need for better management of health information and protection of patient privacy.
Understanding HIPAA is crucial to appreciating its origins and purpose.
Origins and Purpose
Originally, the primary concerns addressed by HIPAA were:
Portability: Portable coverage would ensure that individuals could keep their health insurance if they change jobs or lose a job.
Before HIPAA compliance, employees who changed jobs or were laid off might not have been able to obtain health insurance at a reasonable price because of pre-existing condition exclusions.
Administrative Simplification: Improvement of the efficiency in operation for healthcare providers and insurers by systematizing and standardizing routine transactions, ensuring HIPAA compliance while directing focus that follows through until a claim is fully processed.
Introduction of Privacy and Security Rules
The HIPAA Privacy Rule, part of the broader HIPAA regulations, was introduced by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services in 2003 to institute national standards for protecting each individual’s medical records and personal health information, including data that pass through phone calls between a patient or client (you) with their clinical provider.
This was a major advance in protecting patient privacy and regulating how your health information is used or disclosed.
This was followed in 2005 by the HIPAA Security Rule, another critical aspect of HIPAA regulations, which established standards for protecting ePHI.
This rule focused on implementing technical, administrative, and physical safeguards to protect ePHI from unauthorized access as well as data breaches.
Breach Notification and HITECH Act
The breach notification provisions were enacted as part of the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act in 2009.
This act stated that covered entities needed to let the individuals and HHS if it had any breach in unsecured identity theft (PHI) and informing media, which improved transparency and accountability.
The act also reinforced the adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) and encouraged meaningful use of health IT to support care quality and coordination.

- Lightning-fast speeds to browse without lag
- Servers in 105+ countries around the globe
- Military-grade security to stay safe online
- Try it risk-free with its money-back guarantee
- Native apps for all major devices
HIPAA’s Impact On Healthcare Innovation

HIPAA has significantly influenced healthcare innovation by creating standards that both protect patient privacy and promote the adoption of new technologies. Here is a look at how HIPAA has impacted healthcare revolution:
Adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
Even before 2003, HIPAA required that electronic health information be handled securely, ensuring patient privacy protection.
As a result, EHRs were widely promoted. For example, the Security Rule ensured digital systems would be able to put best practices in place for the safe maintenance of ePHI.
Stimulating healthcare organizations to invest further in digital solutions that streamline data quality, access, and care coordination.
The HITECH Act created additional incentives for implementing EHRs in the meantime, helping to improve patient care quality and efficiency by encouraging “meaningful use” of digital records while maintaining patient privacy protection.
Development of Health Information Technology (HIT)
One could go so far as to claim that HIPAA is single-handedly driving innovation in the Health Information Technology (HIT) space by creating horizontal standards and providing incentives around secure and interoperable systems.
Health information exchanges (HIEs) and patient portals, are up to change the sharing of health data for patients across different providers and platforms.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
HIPAA compliance is driving interest in telemedicine and remote monitoring technology.
By offering HIPAA compliant solutions for telehealth, patient consultations, remote diagnosing and monitoring occur privately while also enabling new access to care.
Telemedicine service providers use innovative telemedicine solutions and stick to the highest forms of encryption that comply with HIPAA regulations.
Enhanced Data Security Measures
The Security Rule of HIPAA paved the way for healthcare to invest more in data security.
This necessity for safeguarding ePHI has resulted in many cutting-edge security technologies, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication and secure cloud storage.
In order to uphold the security of patient information from any breaching and unauthorized entry several measures were taken.
Integration of Big Data and Analytics
HIPAA has played a major role in guiding how we use big data and analytics within healthcare by making sure that standards are met to deal with large amounts of health information securely.
HIPAA regulations not only guarantee that research and analytics data is de-identified or secured but they promote the legitimate use of data to improve patient outcomes, right-size healthcare delivery systems and foster population health improvement.
Compliance and Innovation Challenges
HIPAA has encouraged a number of innovations yet it creates numerous hassles.
Healthcare organizations must balance regulatory compliance with the need for flexibility and creativity in developing new technologies.
But this complexity also results in smarter solutions that make good on their commitment to safeguarding patient rights through highest standards of privacy and security as required by HIPAA compliant integrations.
P.S. HIPAA has played a crucial role in shaping the landscape of healthcare innovation.
Who Falls Under the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
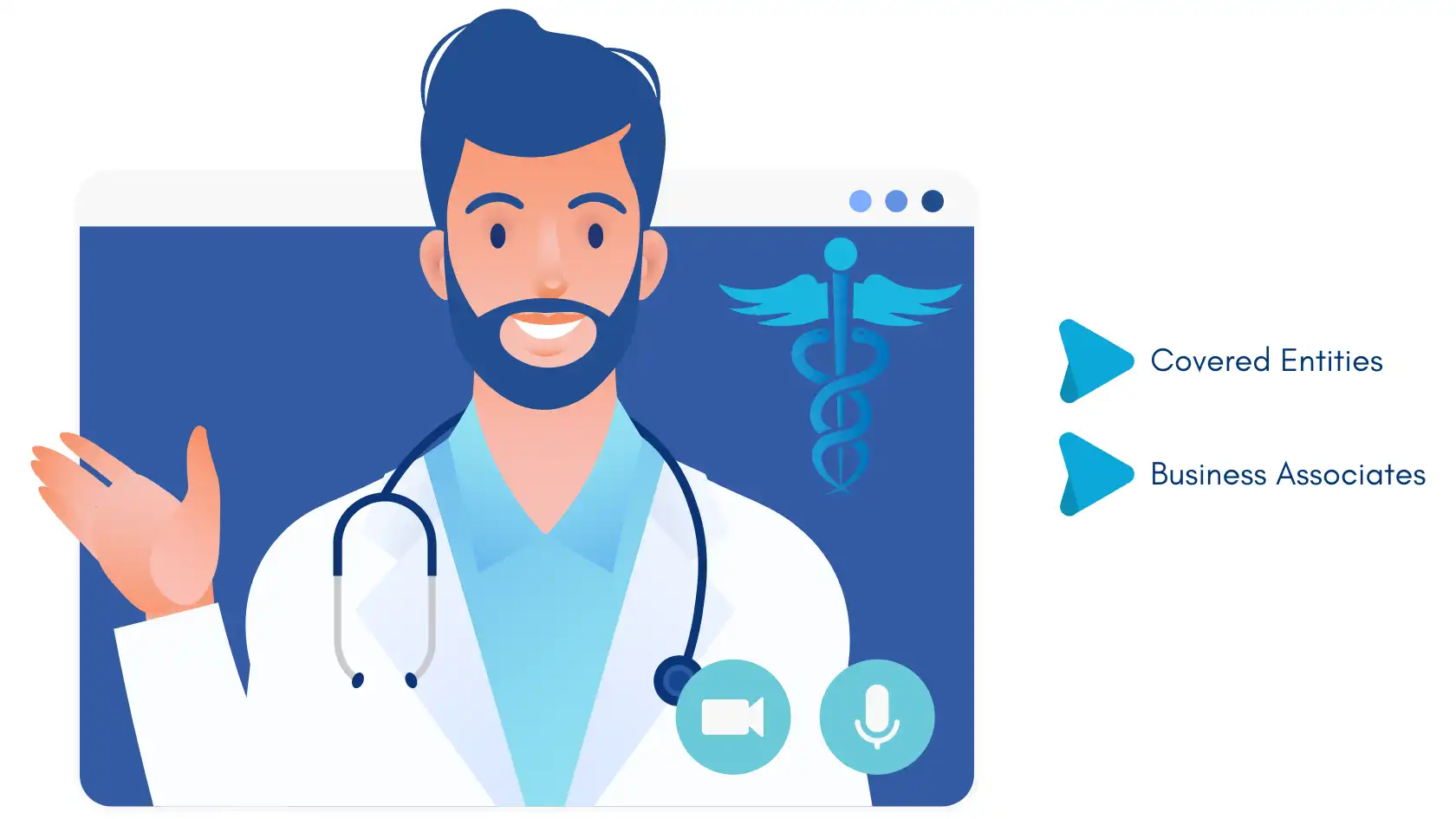

The HIPAA Privacy Rule applies to the following entities:
Covered Entities
Healthcare Providers
A health care provider who transmits any health information in electronic form in connection with a transaction for which the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has adopted standards.
This is for doctors, clinics, hospitals, psychologists, chiropractors, nursing homes, pharmacies and dentists.
Health Plans
Health insurance companies, HMOs, company health plans and government programs that pay for healthcare like Medicare and Medicaid.
Healthcare Clearinghouses
Health Information Exchange Processors which take health information from one entity in nonstandard format and process it into standard format or the reverse.
This includes billing firms, repricing providers and community health information systems.
Business Associates
These are persons or entities who do one of the following on behalf of or provide services to a covered entity that require materials upon which the use and disclosure is not directly performed.
These can be third-party administrators, billing companies and IT service providers.
These are typically subject to the HIPAA privacy rule, which is intended to protect patient access to their personal health records.
Enforcement And Consequences of HIPAA Violations
HIPAA Privacy Rules are from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and Office for Civil Rights (OCR).
They are also responsible for the investigation and resolution of complaints filed by individuals regarding compliance with provisions of HIPAA, as well as conducting administrative actions for enforcing these rules.
What Happens if You Violate HIPAA Privacy Rules?
Civil Penalties
Violations of HIPAA can result in huge civil penalties. These penalties vary depending on the level of negligence and can range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million for repeat violations.
Criminal Penalties
If there is neglect or misconduct, then criminal penalties may be assessed. These permissible penalties for each violation can range from a $50,000 to $250,000 fine and imprisonment of up to 10 years.
Corrective Action Plans
The entity may also be required to create a corrective action plan by the OCR that points to specific deficiencies in its overall privacy practices.
This plan typically involves training employees, updating policies and procedures, and regular testing for compliance with those processes.
Reputational Damage
In addition to potential financial and legal consequences, a HIPAA violation can also tarnish your reputation as an organization, eroding patient trust and scattering patients in search of care elsewhere.
Loss of Business Agreements
Business associates that fail to comply with HIPAA may lose contracts with covered entities, as these entities are required to work only with partners who meet HIPAA standards.

Uninterrupted, high-speed browsing, zero logs so your online activity is always private.
Over 7000 people checked out NordVPN in the last month
Challenges And Criticisms of HIPAA
HIPAA takes great steps to secure health information privacy but still faces many challenges and criticisms. Some of the key issues we examine here:
Complexity and Administrative Burden
The requirements of HIPAA can seem daunting even more so for the small and medium providers.
The specific compliance requirements can create a significant administrative and financial overhead, as entities are required to invest in training systems and processes in order to meet HIPAA standards.
Impact on Innovation
HIPAA has driven healthcare innovation. Given the stringent health information privacy and security requirements, adoption of new technologies could be slow or limited in their function where organizations have to make sure any new systems will support compliance with HIPAA.
Data Breaches and Enforcement
Even HIPAA cannot prevent data breaches which still make headlines each year, sometimes happening due to human error or the lack of proper security mechanisms.
Opponents worry that enforcement and fines will not always serve as a sufficient deterrent or get to the root causes of breaches.
They feel that the fines imposed are not always commensurate with the gravity of their offense.
Balancing Privacy with Data Sharing
The purpose of HIPAA is to protect personal data, some complain that it can make sharing vital health information more difficult than it needs to be.
It can compromise care coordination and impair the ability to mine data for research or population health management initiatives. The search for the sweet spot between privacy and data utility is ongoing.
Variability in State Laws
HIPAA is the federal standard, other states may have their own privacy laws that are more strict.
But this hurts organizations working in multiple states because they have to follow not just federal requirements but a bevy of state regulations.
Evolving Technology and Emerging Threats
The rapid progress of technology and threats on cybersecurity keep creating challenges to meet HIPAA compliance.
Healthcare organizations wanting to remain competitive and protect against emerging cyber risks must constantly update their security practices and learn health sector cybersecurity threats, a resource-heavy process in the face of evolving threats.
Patient Understanding and Engagement
Not all patients may appreciate their rights under HIPAA or possible means to enforce them.
And while education tells patients how to enforce their rights or protect PHI is certainly necessary and good-willed, achieving wide awareness of this type in the population can prove hard.
How Is Data Protected By The HIPAA Privacy Regulations?
The HIPAA Privacy Regulations protect information via the following mechanisms:
Limitations on Use and Disclosure
The Privacy Rule was put in place to limit improper uses and disclosures of protected health information (PHI) by covered entities.
Each time PHI is used or disclosed, it must be limited to only the information necessary for specific purposes like treatment of patient medical conditions and payment received from an insurance company, otherwise a consent should have been obtained from the identified person in question.
Patient Rights
Patients can access and have a copy of their medical records, make corrections to the information in them as needed along with an ability to control how their PHI is shared.
They may also ask for a limit on use and disclosure or choose to receive confidential communications.
Minimum Necessary Standard
Covered entities are also required to take reasonable efforts not only to use PHI but in any disclosure the covered entity makes, they must comply with a rule requiring that they send no more than necessary information so long as the minimum amount of data is sufficient for its intent.
Administrative, Technical and Physical Safeguards
By law, covered entities must employ safeguards to protect PHI. These efforts can be administrative like training for staff, technical like access control or physical controls like secure restricted facility entry.
Business Associate Agreements
These parties are held to the same standards as covered entities when it comes to protecting PHI and therefore must have their own business associate agreements in place.
What Are The Patient Rights Under HIPAA?
Rights conferred to an individual by the HIPAA Privacy Regulations about their PHI these rights include:
Right to Access Health Information
Patient have a right can access his PHI from a doctor or health plan. These include health records, billing information and other documents dealing with healthcare.
Right to Request Corrections
You can make a request to your healthcare provider or health plan for amendments in order to correct inaccuracies within your PHI. The covered entity is required to respond to the request and if appropriate, make the correction.
Right to an Accounting of Disclosures
You have the right to request a list of disclosures that a covered entity has made of your PHI for all purposes other than treatment, payment and health care operations or accounted for by you.
Right to Request Restrictions
You may ask for privacy-designated measures once your PHI sharing and disclosure have been set or made known, banning this information with some family members, not allowing it to be used in certain activities. Where clarified, covered entities are not obligated to agree with all requests but do if it concerns restricting disclosure to a health plan for services paid fully out of pocket by you.
Right to Confidential Communications
The individual may request that a covered entity communicate health information through alternate means or at an alternative location. For example, you can ask that bills be sent to another address and not your home as well, they could use email instead of regular mail.
Right to Receive a Notice of Privacy Practices
Covered entities are required to send individuals covered by the Privacy Rule a notice that explains how their PHI may be used and disclosed, as well as what rights they have in relation to HIPAA. This notice shall be made available at the time of first service encounter and upon request.
Right to File a Complaint
If an individual believes their rights have been violated, that complaint may be filed with the covered entity or directly to OCR. OCR also investigates and enforces HIPAA compliance.
They give rights that allow you to assist in the way your health information is used and protect it, so your privacy is secured and appropriate handling of personal medical data.
New Updates On HIPAA Privacy Rule
As of August 2024, here are some of the latest updates on HIPAA:
Proposed Changes to HIPAA Privacy Rule
The update to the HIPAA Privacy Rule proposed by the U.S. The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) aims at increasing patient’s access to their health information as well as for advancing system interoperability goals. The proposed changes include:
Reducing Barriers to Access: Patients should have easier ways of obtaining their health information including lowering fees charged for accessing records, while electronic access could be available in a manner that improves upon current processes related to non-electronic requests.
Improving Interoperability: Making it easier for health systems to share data among themselves keeping patient privacy.
New Cybersecurity Guidelines
In the wake of a rising tide of cyberattacks, HHS has published new cybersecurity guidelines designed to assist covered entities and business associates in shoring up their defenses. These guidelines focus on:
AI and Cybersecurity: Integrating AI technologies to enhance threat detection and response capabilities, offering businesses a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Risk Assessment: To improve risk assessment methodology to help in recognizing weaknesses and introducing danger moderation.
Expansion of Telehealth Regulations
The rise of telehealth services came alterations in HIPAA regulations to consider nuances associated with virtual care. Recent updates include:
Telehealth Security: Increased security requirements to protect ePHI on telehealth platforms.
Patient Consent: Amending consent regulations to account for the virtual nature of telehealth appointments.
Increased Enforcement and Penalties
The Office for Civil Rights (OCR) has intensified enforcement efforts, with an emphasis on:
High-Profile Cases: Addressing high-profile cases of non-compliance and applying larger fines.
Regular Audits: Conduct more frequent audits to make sure that they are keeping on to HIPAA regulations.
Focus on Data Privacy and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
As AI technologies are becoming more integrated into healthcare, HIPAA has updated to address privacy concerns related to AI:
Data Handling: Ethical use of AI in healthcare and data security for patients.
Transparency: Making AI systems in healthcare accountable, especially about how they use and process PHI.
These recent modifications show how HIPAA continues to change with the times, expanding if you will, modernizing healthcare and keeping up with new technologies while safeguarding patient privacy.
FAQs
What is the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
What are the three main rules of HIPAA?
What does HIPAA protect the privacy of?
What is HIPAA and what is its purpose?
What does HIPAA stand for?
Who is covered by HIPAA?
Conclusion
We’ve covered a lot of ground in our deep dive into HIPAA’s Privacy Rule. We have shown how HIPAA guards your health data, putting strong limits on what can be done with it and to whom it may be disclosed.
Sort of like your very own secret service for medical records. But behind the privacy shield of HIPAA, is a powerful tool that belongs to you.
You have the right to view your own health information, request corrections in healthcare reports and even direct how that data is shared under HIPAA. It is like you are the CEO of your healthcare data.
The next time you drop by your doctor’s place or are to fill a medical form, spare some thought for all the ways in which HIPAA protects your private data.
Be sure that the confidentiality of your health profile is in safe hands. If at any time you have questions or concerns about your HIPAA rights, ask.
Now off with you to take advantage of the awesomeness that is HIPAA Privacy Rule.